Flanking structure and single layer fold development in isotropic and anisotropic rock
Descrição
Flanking structures around planar discontinuities in an otherwise homogeneous ow develop a characteristic geometry that is potentially a source of kinematic information about the background ow. Analytical methods were used to calculate the velocity around a thin weak inclusion (representing a fracture) in linear viscous material. This approach allows modelling of anking structures to very large strains. The velocity eld around a given anking structure can be calculated for the complete range of potential background ow elds, provided that the orientation of the fabric attractor and the bulk shear sense are known. Structures can be undeformed according to these velocity elds and, by quantifying the mis t between the actual and initial geometry, the vorticity number of the ow eld and the duration of deformation accurately determined. With these two parameters established, the background (bulk) deformation involved in the formation of a speci c anking structure can be calculated. This chapter was published in Journal of Structural Geology (Kocher and Mancktelow, 2005)

Patterning and folding of intestinal villi by active mesenchymal dewetting

Flanking structure and single layer fold development in isotropic and anisotropic rock

Transtensional flanking structures - ScienceDirect

Flanking structure and single layer fold development in isotropic and anisotropic rock
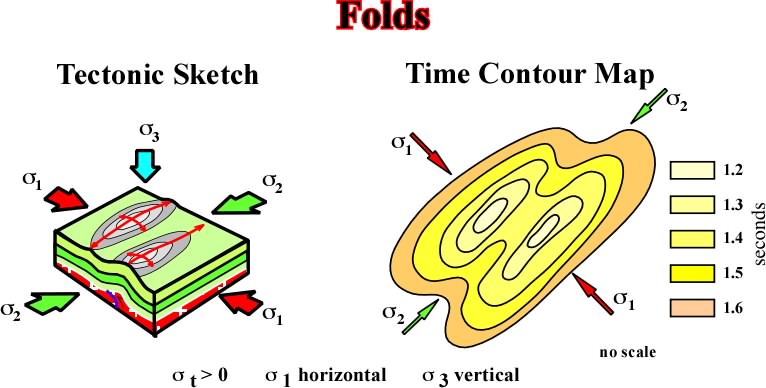
BasPrincTectonics6
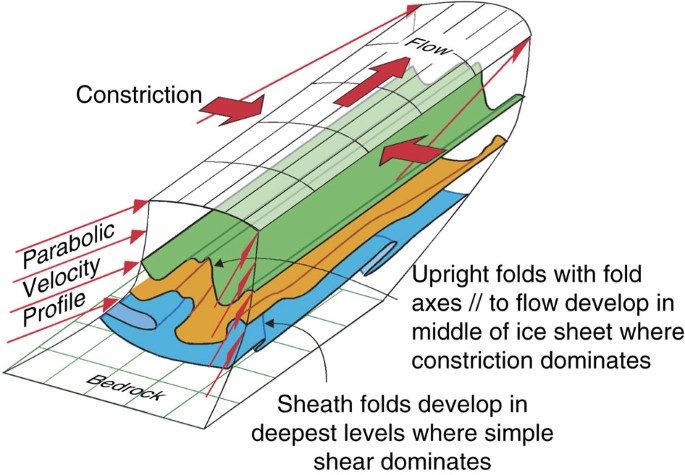
Converging flow and anisotropy cause large-scale folding in Greenland's ice sheet

Transtensional origin of multi-order cross-folds in a high-grade gneiss complex, southwestern Grenville Province: formation during post-peak gravitational collapse

Transtensional origin of multi-order cross-folds in a high-grade gneiss complex, southwestern Grenville Province: formation during post-peak gravitational collapse

Flanking structure and single layer fold development in isotropic and anisotropic rock
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)