Labetalol infusion for refractory hypertension causing severe hypotension and bradycardia: an issue of patient safety, Patient Safety in Surgery
Descrição
Incremental doses of intravenous labetalol are safe and effective and, at times, such therapy may need to be augmented by a continuous infusion of labetalol to control severe hypertension. Continuous infusions of labetalol may exceed the recommended maximum daily dose of 300 mg on occasion. We report a case in which hypertension occurring after an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair, initially responsive to intermittent intravenous beta-blockade, became resistant to this therapy leading to the choice of an intravenous labetalol infusion as the therapeutic option. The labetalol infusion resulted in a profound cardiovascular compromise in this postoperative critically ill patient. While infusions of labetalol have successfully been used, prolonged administration in the intensive care unit requires vigilance and the establishment of a therapeutic rationale/policy for interventions, such as the ready availability of glucagon, β-agonists, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, insulin, and vasopressin when severe cardiovascular depression occurs.

Part 7.3: Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and Tachycardia

Hypertension Blood Pressure - Cancer Therapy Advisor

2023 American Heart Association Focused Update on the Management of Patients With Cardiac Arrest or Life-Threatening Toxicity Due to Poisoning: An Update to the American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and

Pharmacology Basicmedical Key

LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
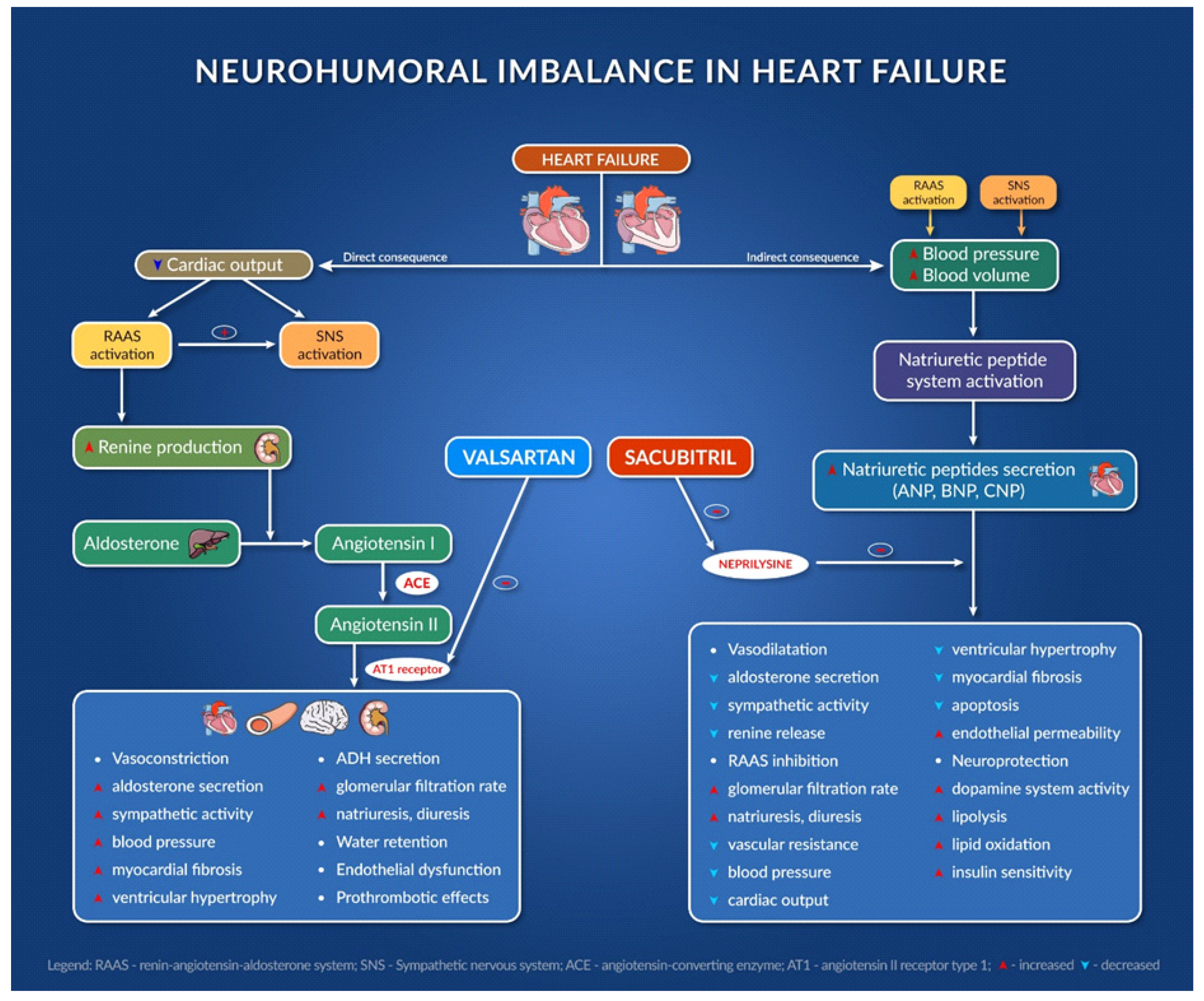
JCM, Free Full-Text

Hypertensive emergency - EMCrit Project

LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP
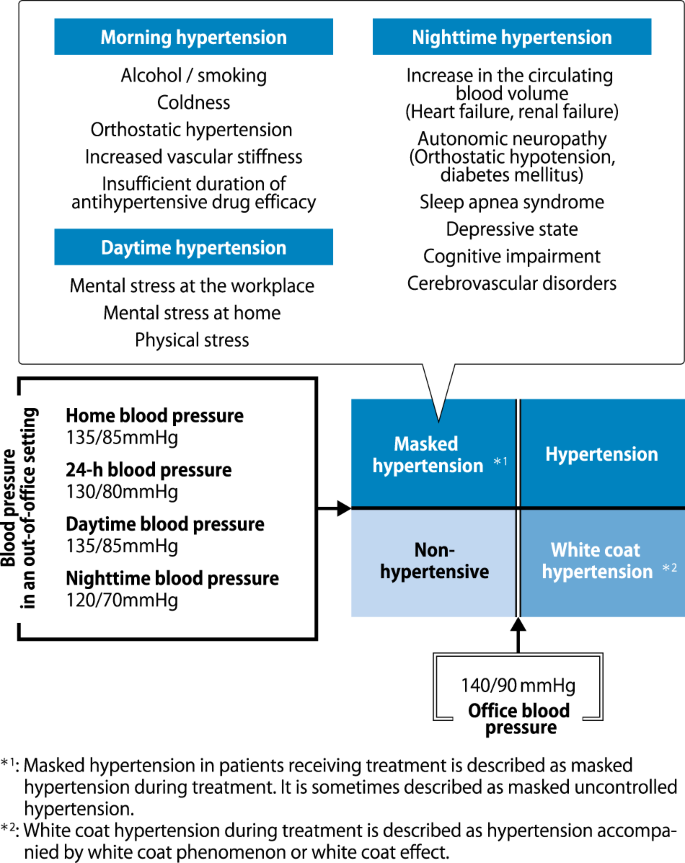
The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019)

– Emergency Medicine EducationEclampsia in the ED: Presentation, Differential Diagnosis, and Treatment - - Emergency Medicine Education
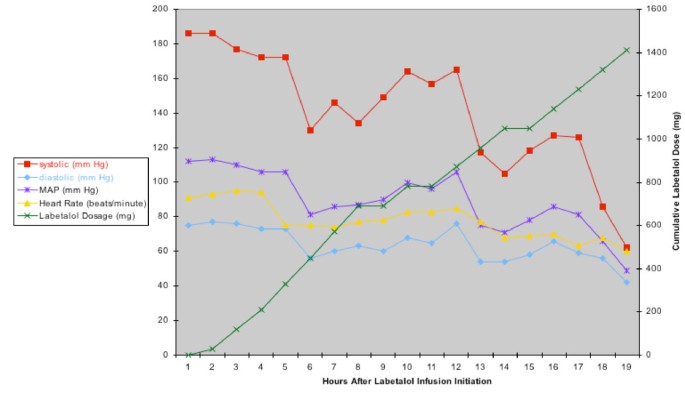
Labetalol infusion for refractory hypertension causing severe hypotension and bradycardia: an issue of patient safety, Patient Safety in Surgery
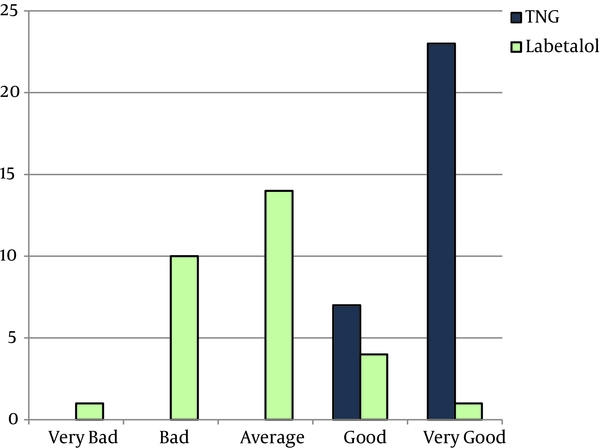
Comparing Labetalol and Nitroglycerine on Inducing Controlled Hypotension and Intraoperative Blood Loss in Rhinoplasty: A Single-Blinded Clinical Trial, Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine

LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION, USP

Continuous-Infusion Labetalol vs Nicardipine for Hypertension Management in Stroke Patients - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)