Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Descrição
Bovine anaplasmosis is a tick-borne disease caused by an obligate intercellular Gram-negative bacterium named Anaplasma (A.) marginale. In this study, we report the seasonal prevalence, potentially associated risk factors and phylogeny of A. marginale in cattle of three different breeds from Multan District, Southern Punjab, Pakistan. A total of 1020 blood samples (crossbred, n = 340; Holstein Friesian, n = 340; and Sahiwal breed, n = 340) from apparently healthy cattle were collected on a seasonal basis from March 2020 to April 2021. Based on PCR amplification of the msp5 partial sequence, overall, the A. marginale prevalence rate was estimated at 11.1% (113/1020) of the analyzed cattle samples. According to seasons, the highest prevalence rate was observed in autumn (16.5%), followed by winter (10.6%) and summer (9.8%), and the lowest was recorded in the spring (7.5%). The crossbred and Sahiwal cattle were the most susceptible to A. marginale infection, followed by Holstein Friesian cattle (7.9%). Analysis of epidemiological factors revealed that cattle reared on farms where dairy animals have tick loads, dogs coinhabit with cattle and dogs have tick loads have a higher risk of being infected with A. marginale. In addition, it was observed that white blood cell, lymphocyte (%), monocyte (%), hematocrit, mean corpuscular hemoglobin and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentrations were significantly disturbed in A. marginale-positive cattle compared with non-infested cattle. Genetic analysis of nucleotide sequences and a phylogenetic study based on msp5 partial sequencing demonstrated that this gene appears to be highly conserved among our isolates and those infecting apparently healthy cattle from geographically diverse worldwide regions. The presented data are crucial for estimating the risk of bovine anaplasmosis in order to develop integrated control policies against bovine anaplasmosis and other tick-borne diseases infecting cattle in the country.
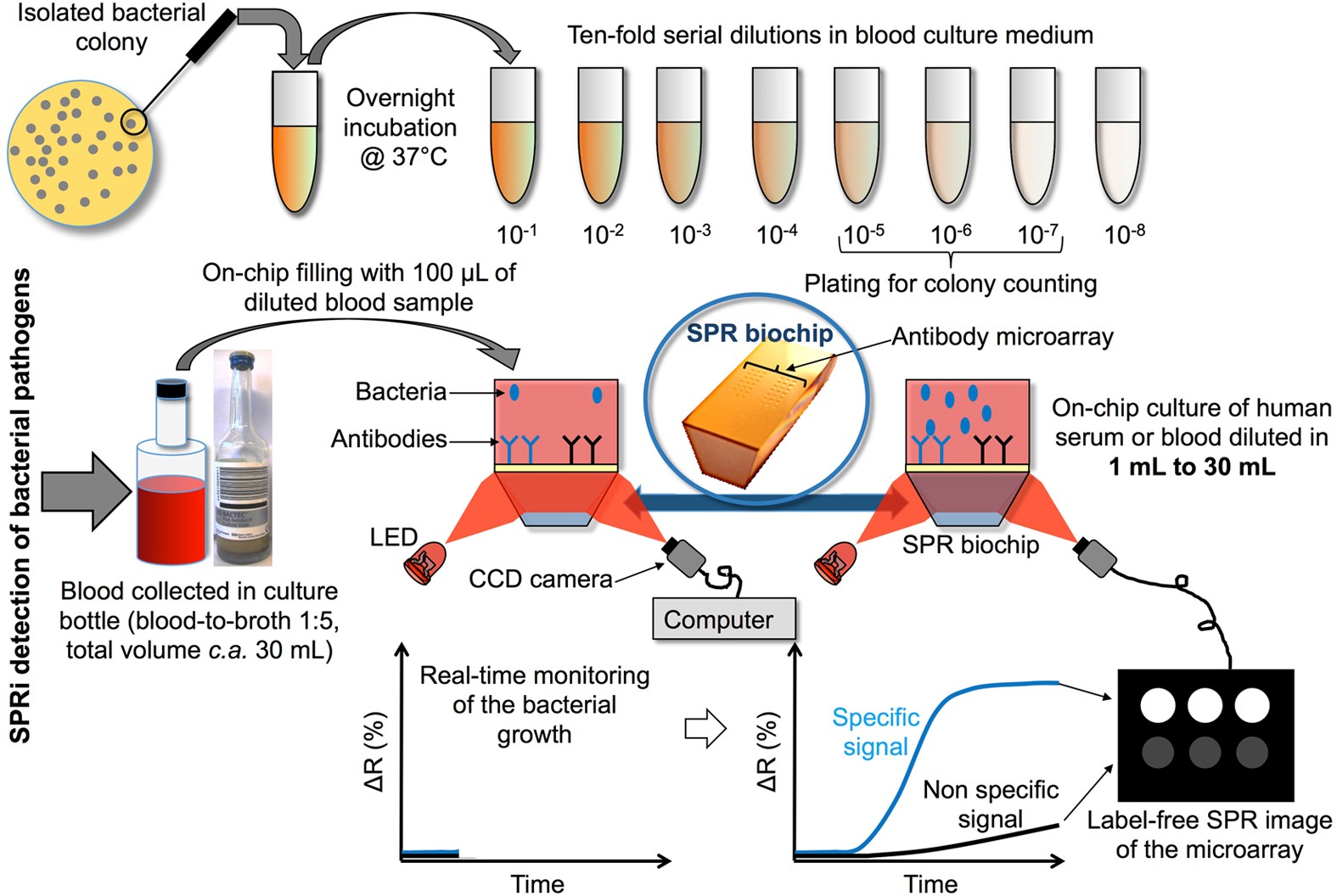
Biochips for Direct Detection and Identification of Bacteria in
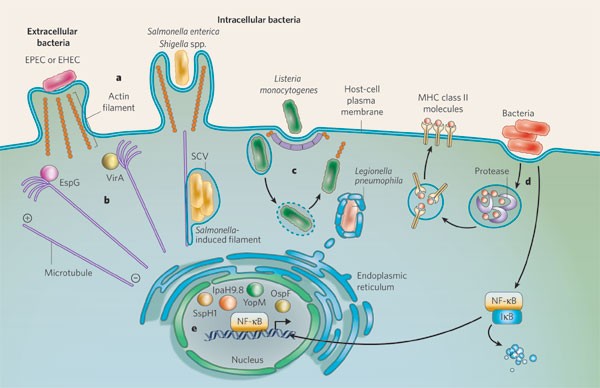
Manipulation of host-cell pathways by bacterial pathogens

Solved 1. What is epithelia, what is an example of

Bacterial Invasion: The Paradigms of Enteroinvasive Pathogens

Microbial Minimalism: Genome Reduction in Bacterial Pathogens
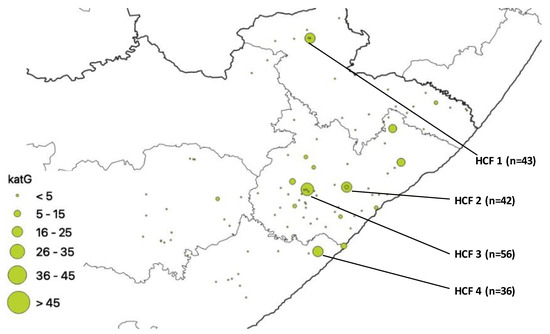
Hcf Practice Maps - Colaboratory
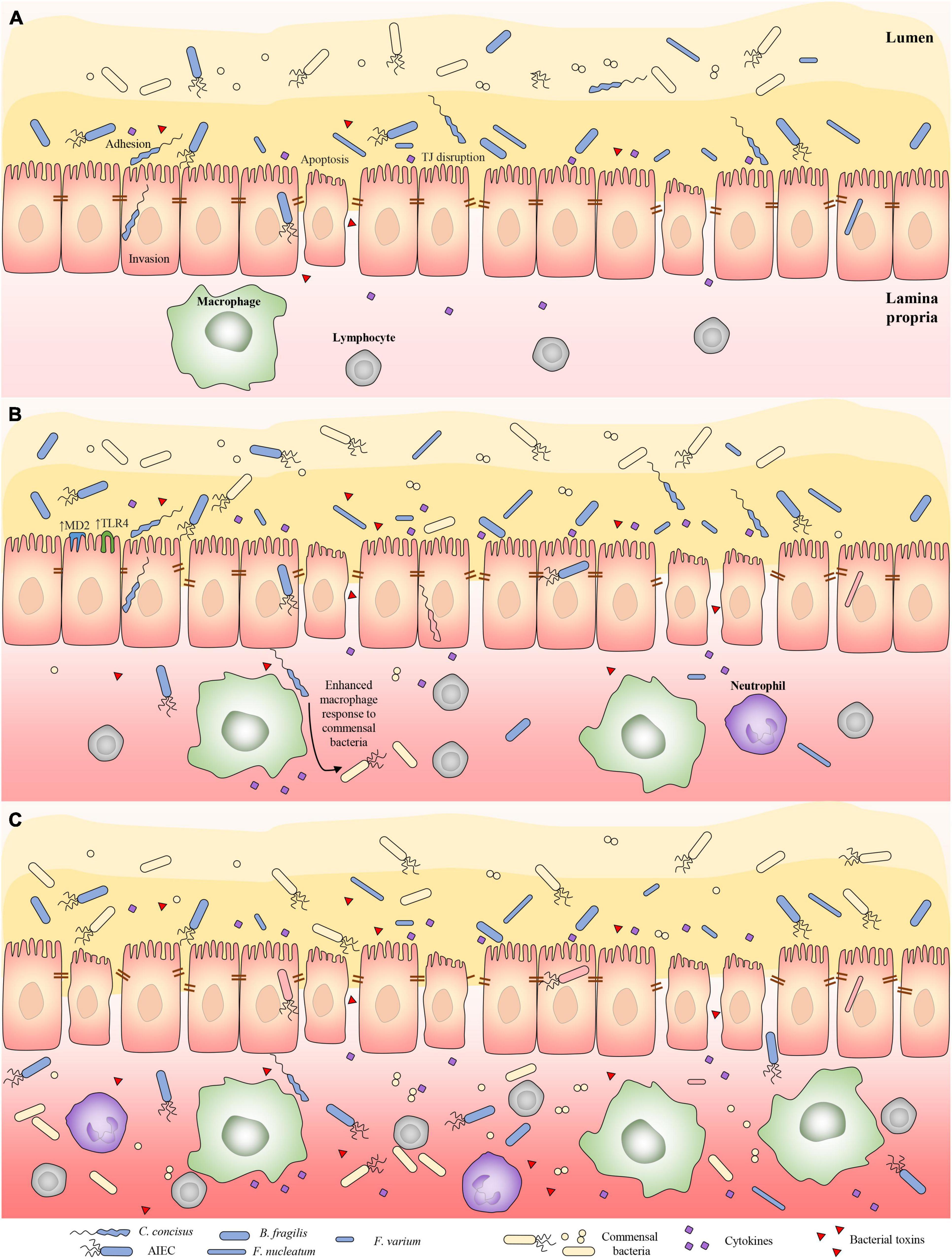
Frontiers Bacterial Species Associated With Human Inflammatory
Pathogen CK-12 Foundation

Free Google Slides and PowerPoint templates about bacteria
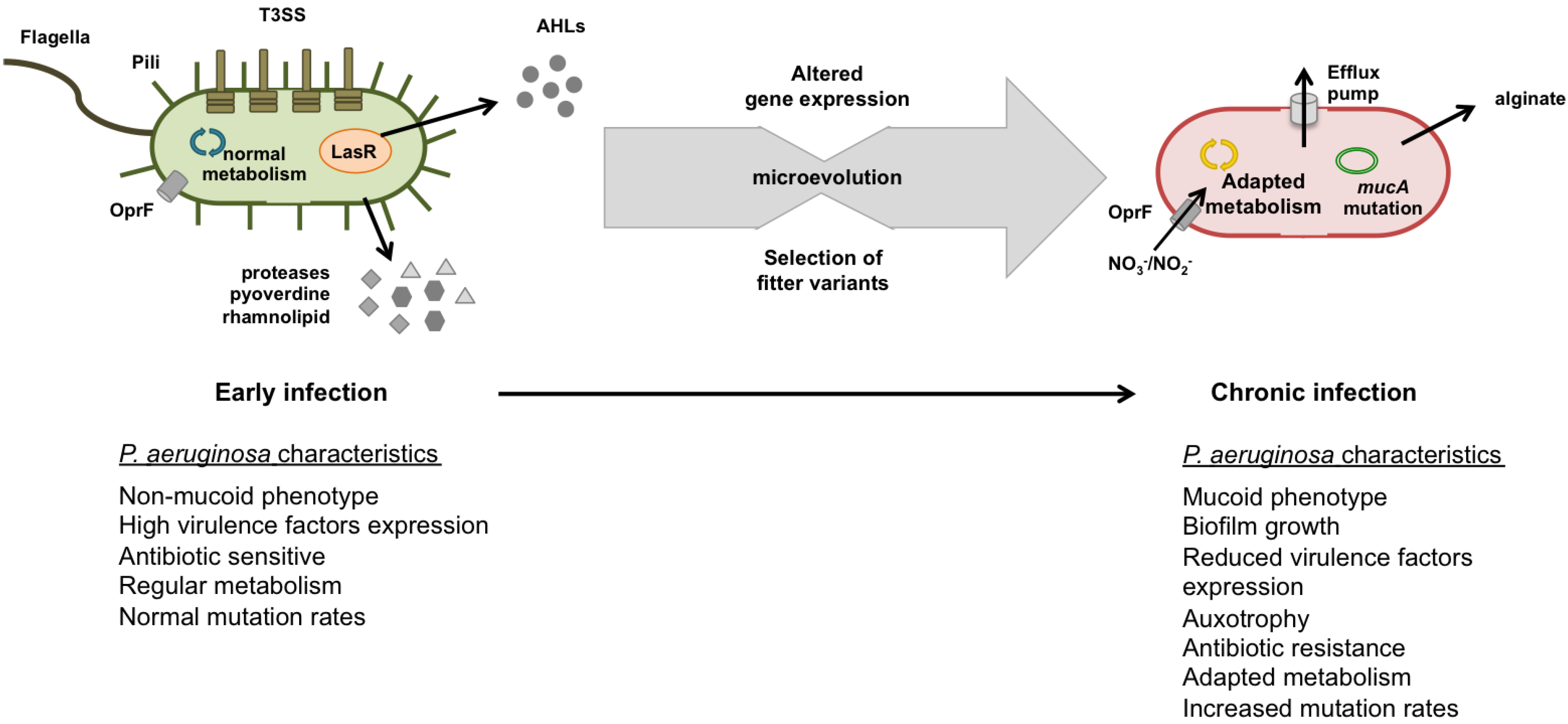
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Southeastern Naturalist, Volume 15, Number 1 (2016): N4–N6

Sequential Infection with Common Pathogens Promotes Human-like

Bloodborne Pathogens Handouts, First Aid
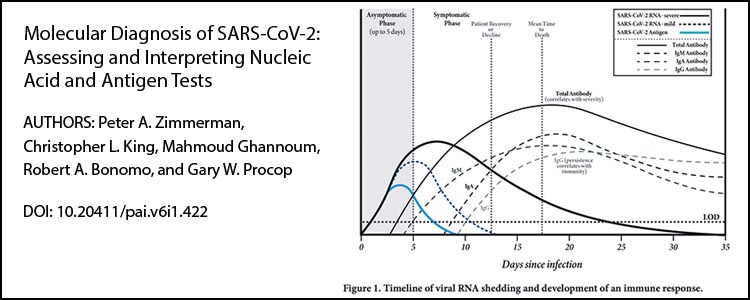
Pathogens and Immunity
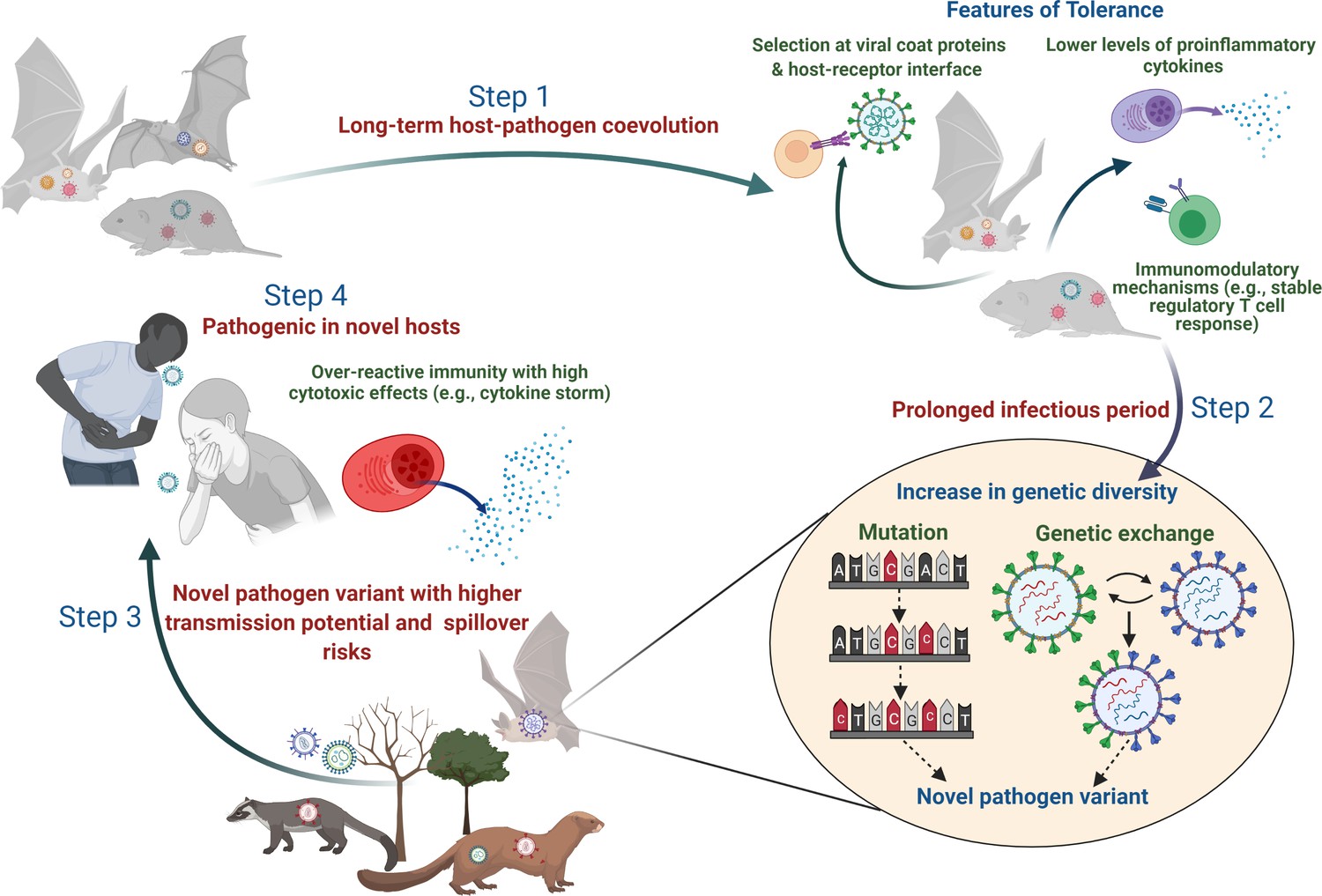
Evolution of pathogen tolerance and emerging infections: A missing
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







