JPM, Free Full-Text
Descrição
Congenital heart diseases (CHDs) are structural or functional defects present at birth due to improper heart development. Current therapeutic approaches to treating severe CHDs are primarily palliative surgical interventions during the peri- or prenatal stages, when the heart has fully developed from faulty embryogenesis. However, earlier interventions during embryonic development have the potential for better outcomes, as demonstrated by fetal cardiac interventions performed in utero, which have shown improved neonatal and prenatal survival rates, as well as reduced lifelong morbidity. Extensive research on heart development has identified key steps, cellular players, and the intricate network of signaling pathways and transcription factors governing cardiogenesis. Additionally, some reports have indicated that certain adverse genetic and environmental conditions leading to heart malformations and embryonic death may be amendable through the activation of alternative mechanisms. This review first highlights key molecular and cellular processes involved in heart development. Subsequently, it explores the potential for future therapeutic strategies, targeting early embryonic stages, to prevent CHDs, through the delivery of biomolecules or exosomes to compensate for faulty cardiogenic mechanisms. Implementing such non-surgical interventions during early gestation may offer a prophylactic approach toward reducing the occurrence and severity of CHDs.
J.P. Morgan Wealth Plan
JPM, Free Full-Text

Model Portfolios J.P. Morgan Asset Management
VA's Multidisciplinary Approach Proves to Be Best for Adult SMA
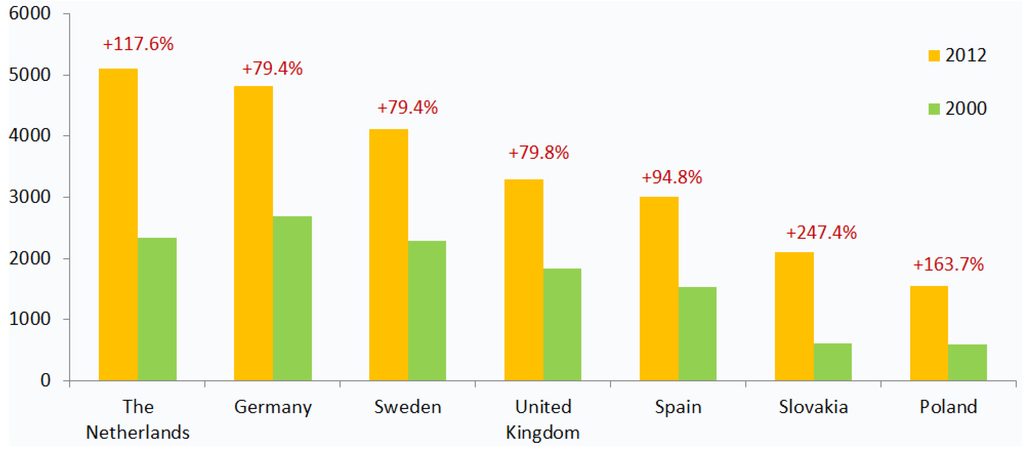
JPM, Free Full-Text
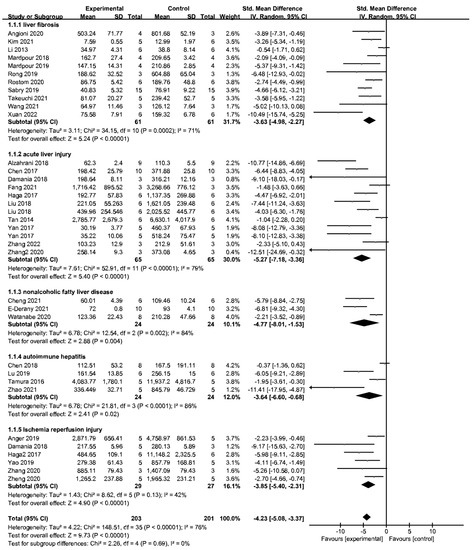
Getdata Graph Digitizer 2.23 - Colaboratory

Jamie Dimon's Letter to Shareholders, Annual Report 2022
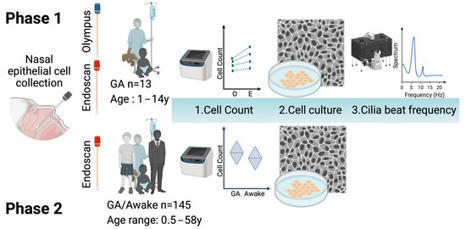
Mucosal Immunity, Page 3

JPM, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)