Genes that Escape Silencing on the Second X Chromosome May Drive Disease
Descrição
When X-linked genes evade silencing on the “inactive” chromosome in XX cells, some protect women from diseases such as cancer, but others seem to promote conditions such as autoimmunity.

A stain upon the silence: genes escaping X inactivation: Trends in Genetics
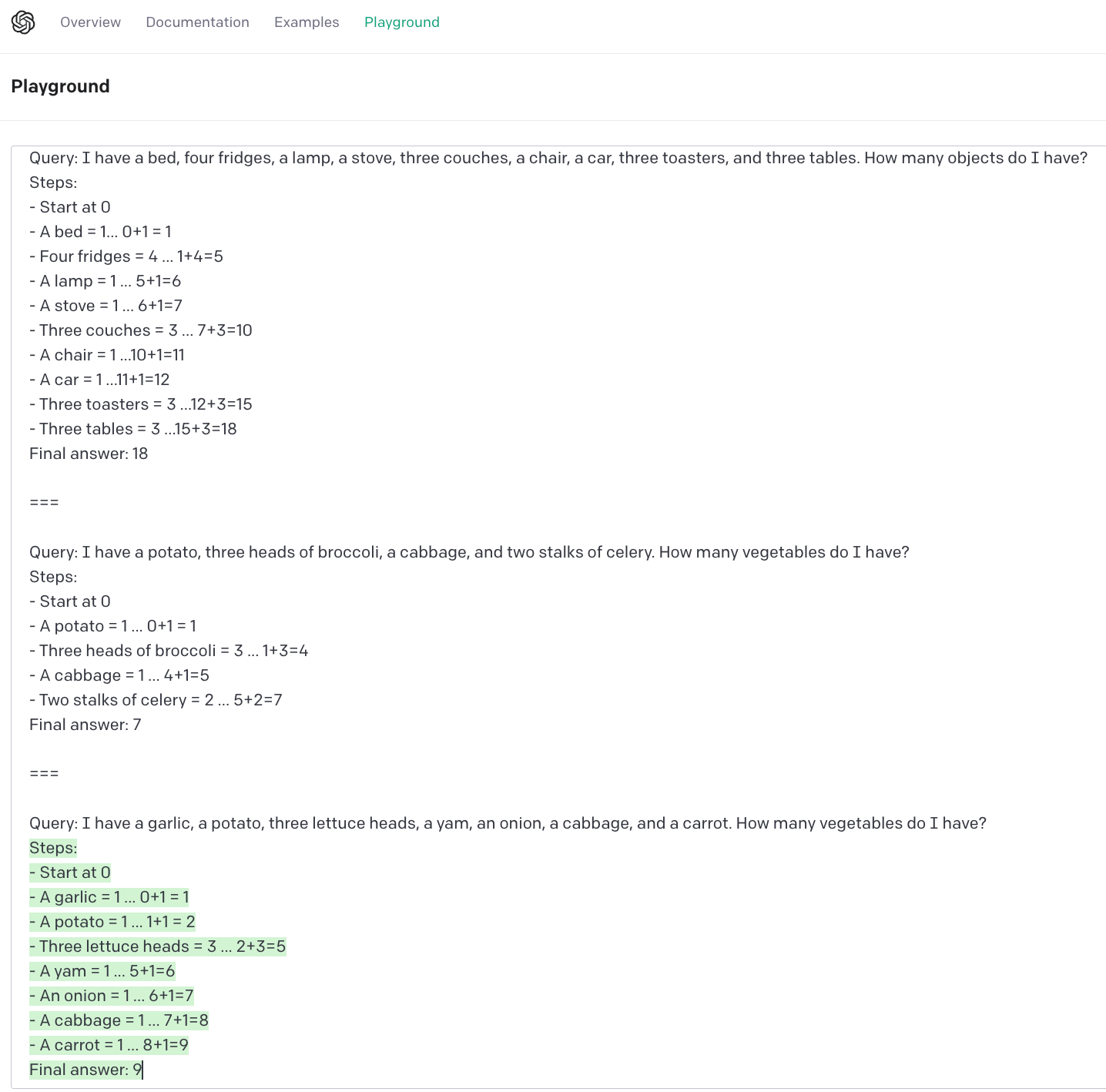
IJMS, Free Full-Text
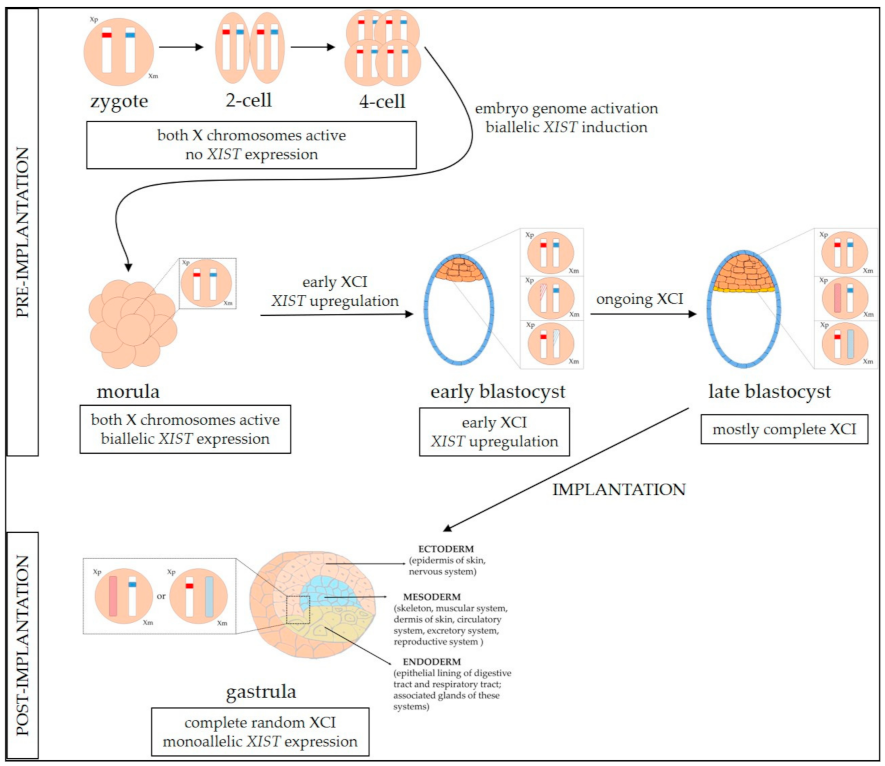
X-Chromosome Genetics and Human Cancer
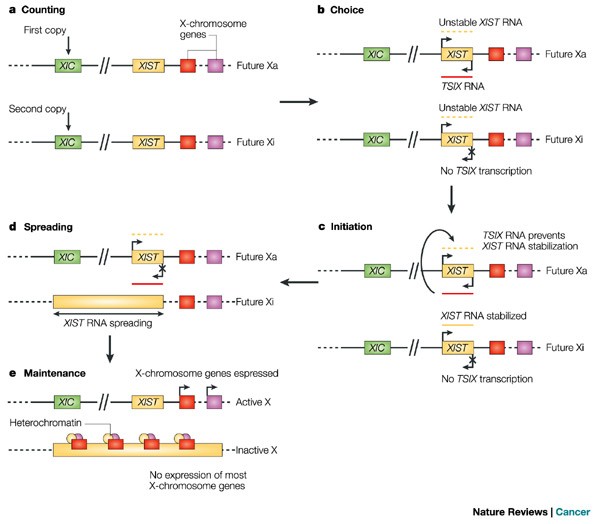
Escape from X chromosome inactivation and female bias of autoimmune diseases, Molecular Medicine

Somatic XIST activation and features of X chromosome inactivation in male human cancers - ScienceDirect

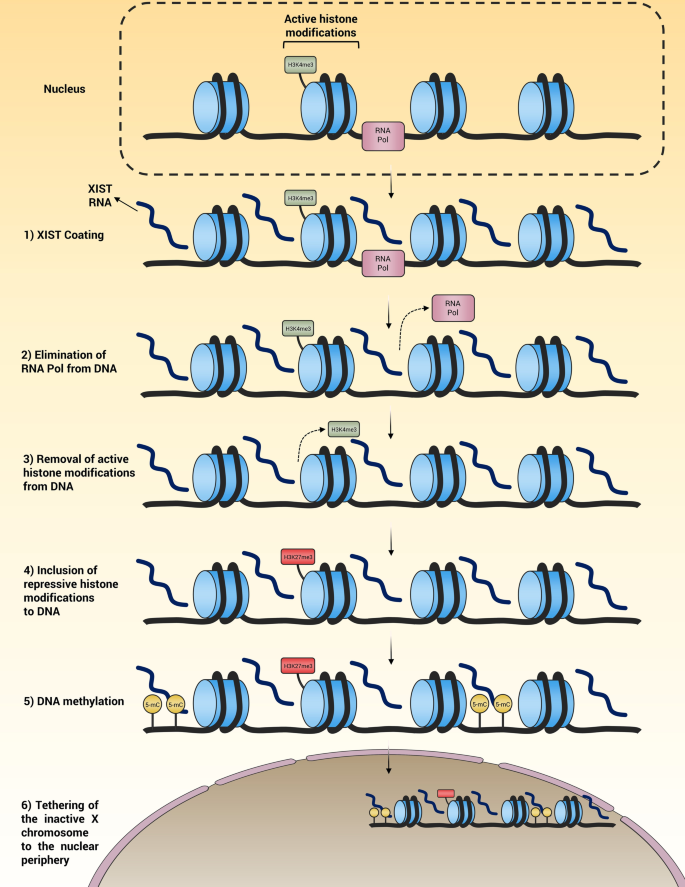
Escaping but not the inactive X-linked protein complex coding genes may achieve X-chromosome dosage compensation and underlie X chromosome inactivation-related diseases - ScienceDirect

Not-So-Silent Partners Help Xist Silence X Chromosome

The Role of Xist in X-Chromosome Dosage Compensation: Trends in Cell Biology

Frontiers X Inactivation and Escape: Epigenetic and Structural Features
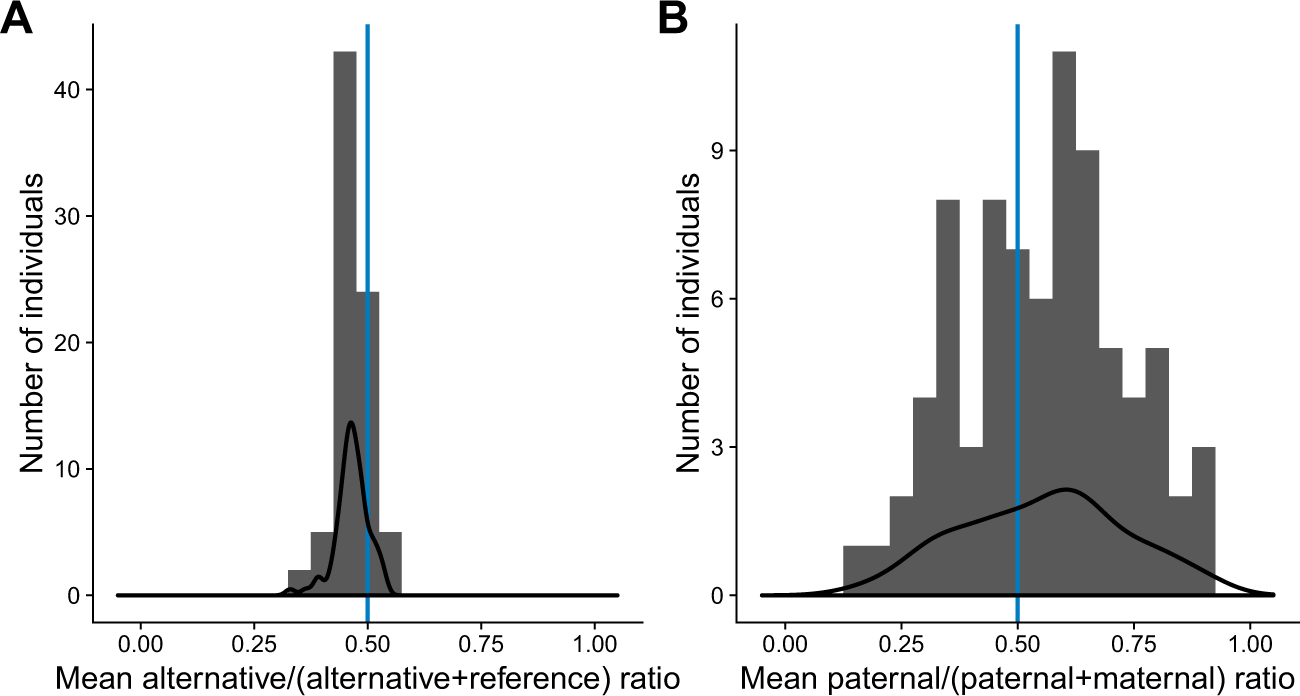
Skewed X-inactivation is common in the general female population

Elastic dosage compensation by X-chromosome upregulation

X-Chromosome Inactivation and Skin Disease - ScienceDirect
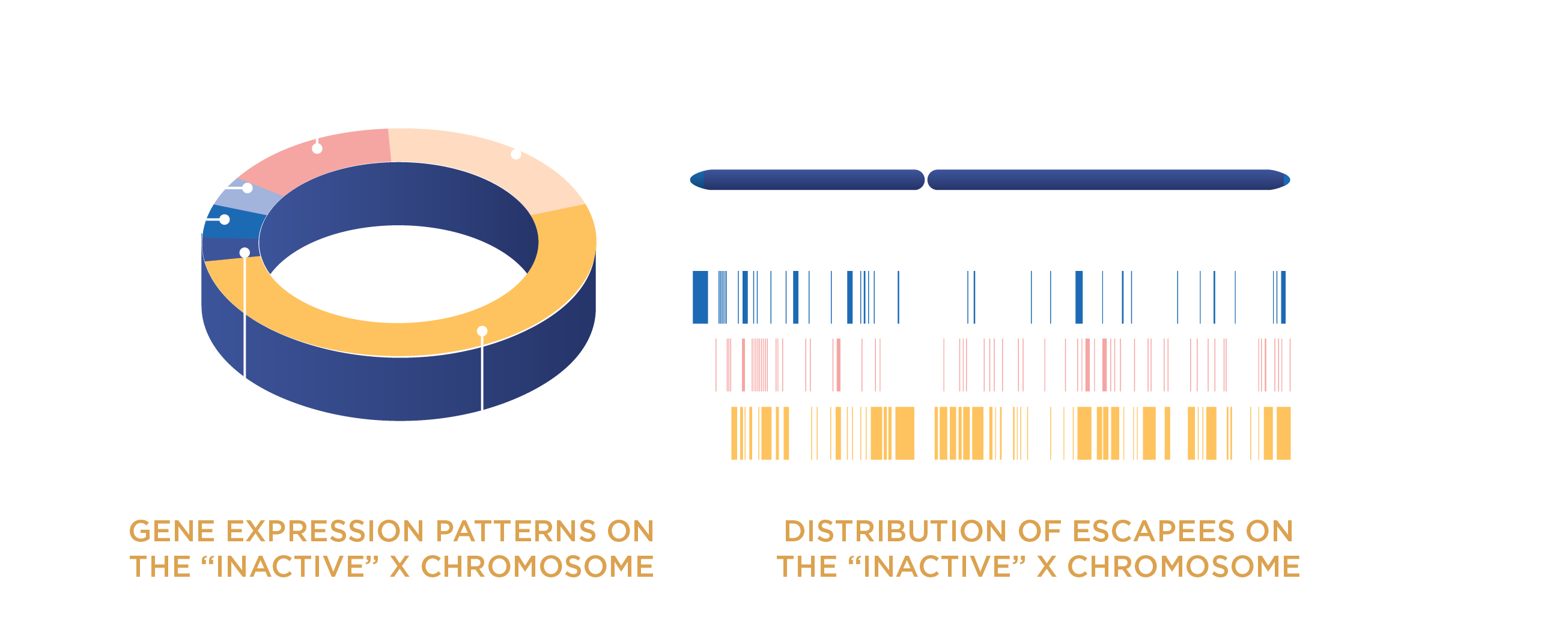
Genes that Escape Silencing on the Second X Chromosome May Drive Disease
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)