A comparison of Esmolol and Labetalol for Attenuation of Sympathomimetic Responses to Laryngoscopy and Intubation
Descrição
Both Labetalol and Esmolol in low doses are not effective in attenuation of sympathomimetic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation. ABSTRACT: Objective: The study was designed to Compare esmolol and labetolol for attenuation of sympathomimetic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation. Materials & Methods: 80 patients were randomly divided into two groups by prospective randomized single blind study, 40 patients received labetolol 0.5mg/kg and other patients received esmolol 0.25mg/kg. The baseline heart rate, BP, Spo2 were recorded & Compared. Conclusion: both Labetalol ( 0.25mg/kg ) and Esmolol (0.5 mg/kg ) in low doses are not effective in attenuation of sympathomimetic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation .

To evaluate the efficacy between 0.15mg/Kg and 0.25mg/Kg of iv labetalol in the suppression of haemodynamic response to extubation - IJCA

Comparison of esmolol and labetalol, in low doses, for attenuation of sympathomimetic response to laryngoscopy and intubation
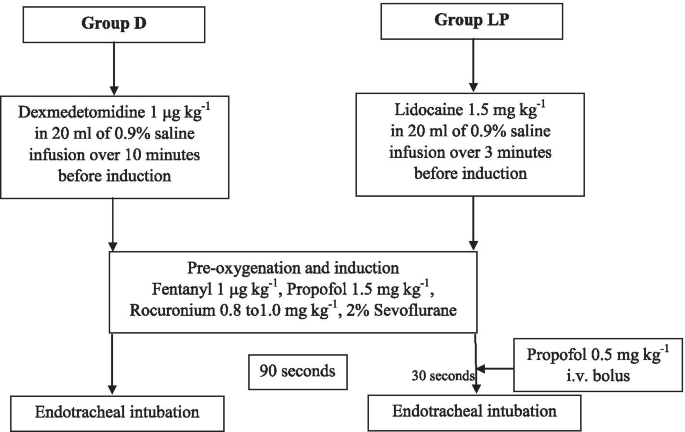
Comparison of the hemodynamic response of dexmedetomidine versus additional intravenous lidocaine with propofol during tracheal intubation: a randomized controlled study, BMC Anesthesiology

Comparison of esmolol and labetalol, in low doses, for attenuation of sympathomimetic response to laryngoscopy and intubation
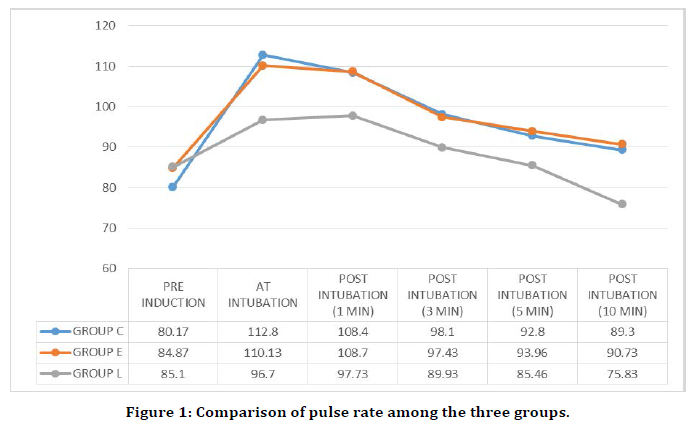
Comparision of Esmolol and Labetalol in Low Doses for Attenuation of Sympathomimetic Response to Laryngoscopy and Intubation
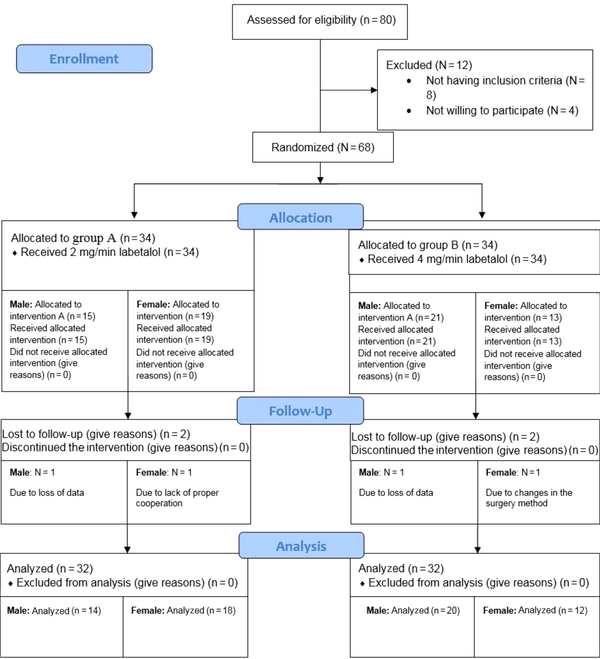
Comparison of the Effect of Two Different Doses of Labetalol to Induce Controlled Hypotension on Hemodynamic Changes During Spinal Fusion Surgery, Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine

PDF) Attenuation of hypertensive response with esmolol and labetalol in low doses in orotracheal intubation: A comparative study

A Comparative Study of Intravenous Esmolol, Labetalol and Lignocaine in Low Doses for Attenuation of Sympathomimetic Responses to Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation
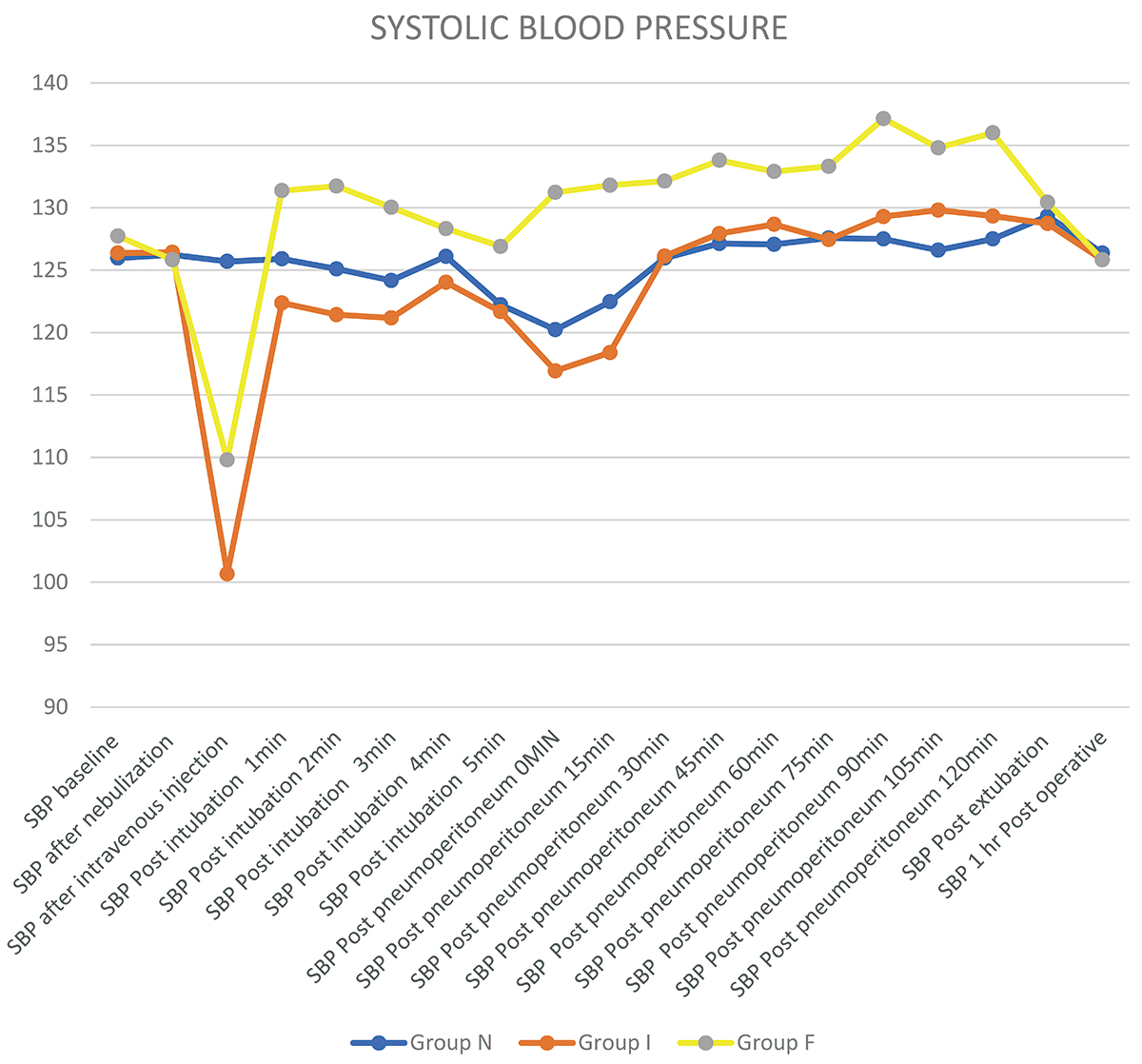
Comparison of Hemodynamics and Opioid Sparing Effect of Dexmedetomidine Nebulization and Intravenous Dexmedetomidine in Laparoscopic Surgeries Under General Anesthesia
Dexmedetomidine vs. Fentanyl-Midazolam Combination to Mitigate the Stress Response in Microlaryngoscopy: A Randomized Double-blind Clinical Trial, Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine

Comparision Of Esmolol and Labetalol In Low Doses For Attenuation Of Sympathomimetic Response To Laryngoscopy And Intubation

Ivabradine versus propranolol given orally in microlaryngoscopic surgeries in attenuating stress response: A comparative prospective double blind randomized study - ScienceDirect

PDF) Attenuation of hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation -comparison of fentanyl, esmolol and metoprolol in normotensive individuals
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)