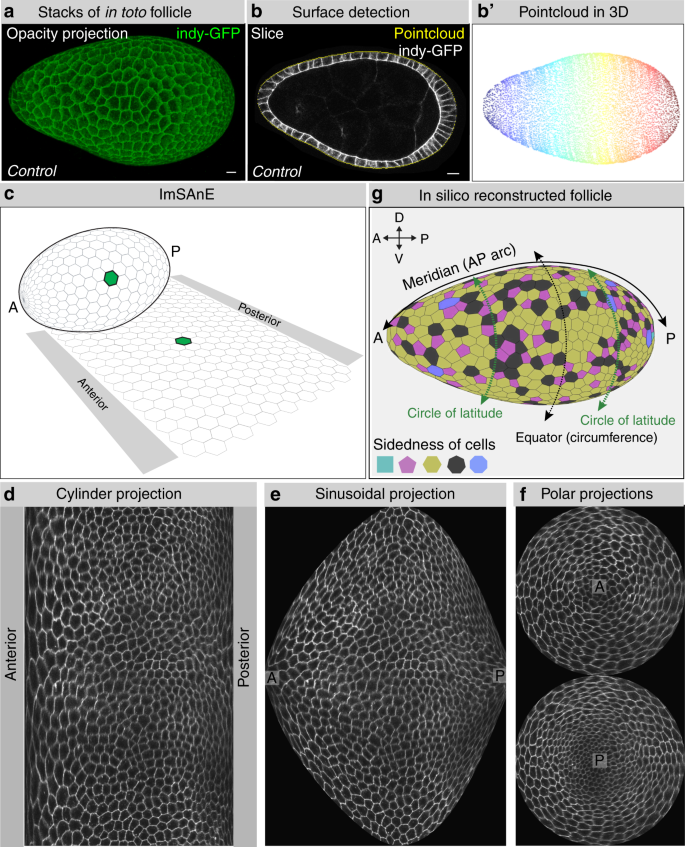
Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Descrição

Spreading of cells correlates with hydrogel stiffness. (A) Phase
Cells, Free Full-Text
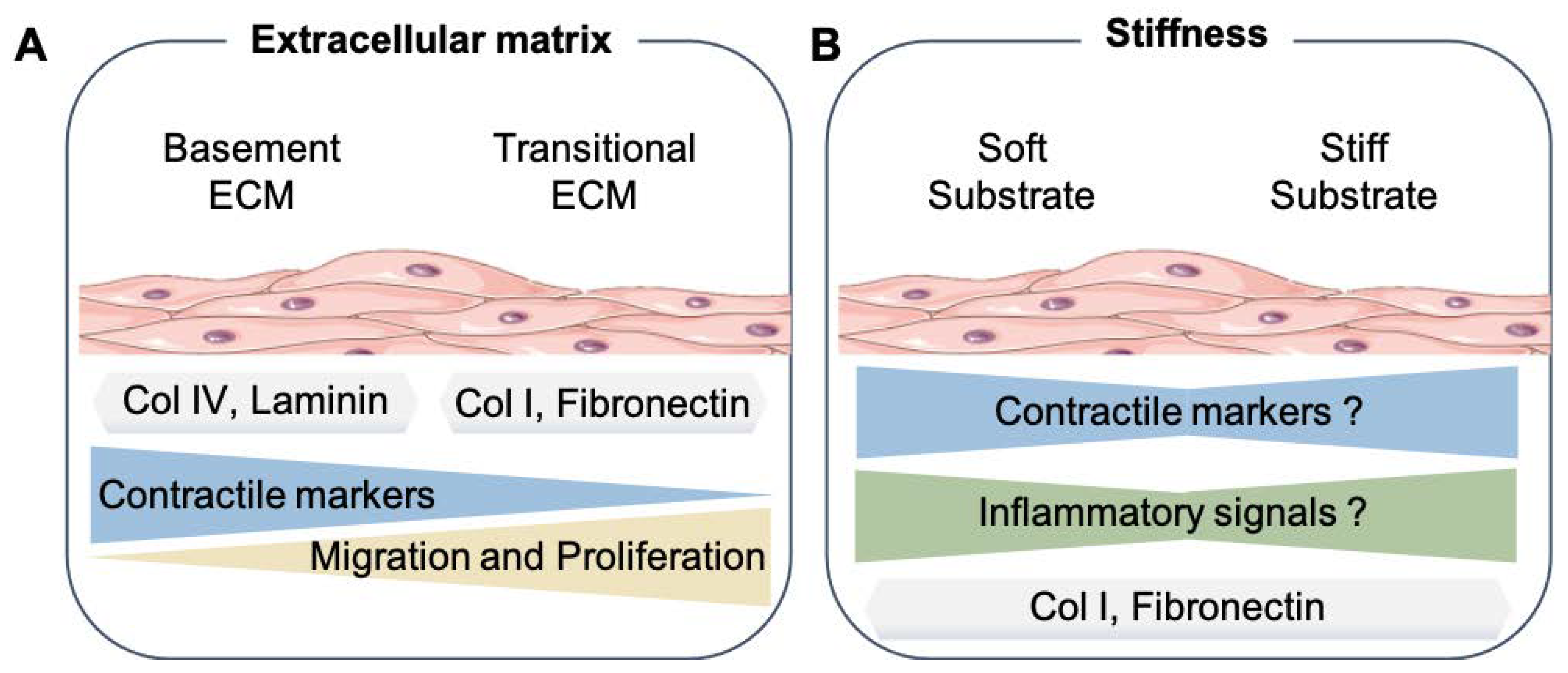
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation
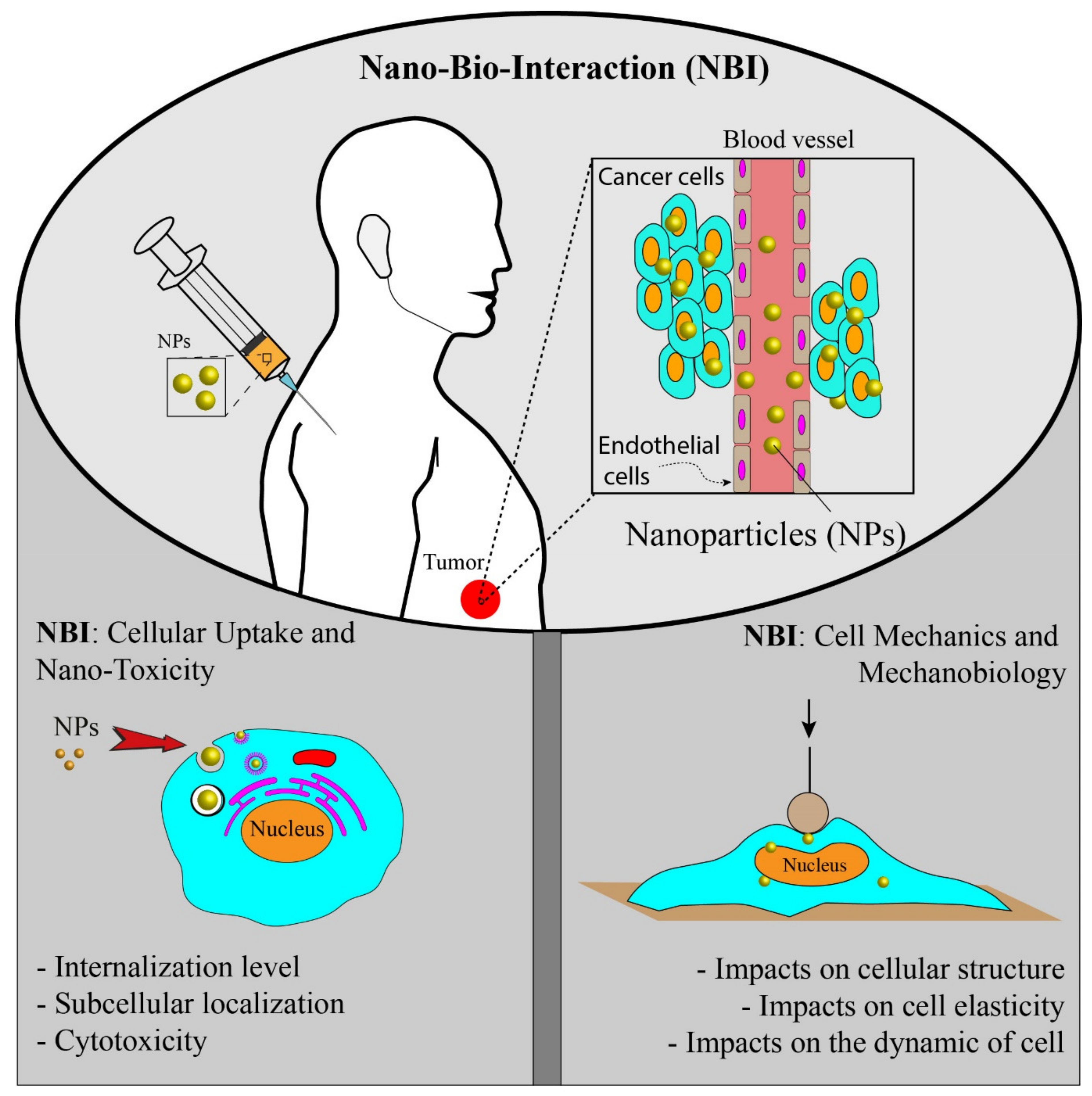
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Stiffness Sensing by Cells
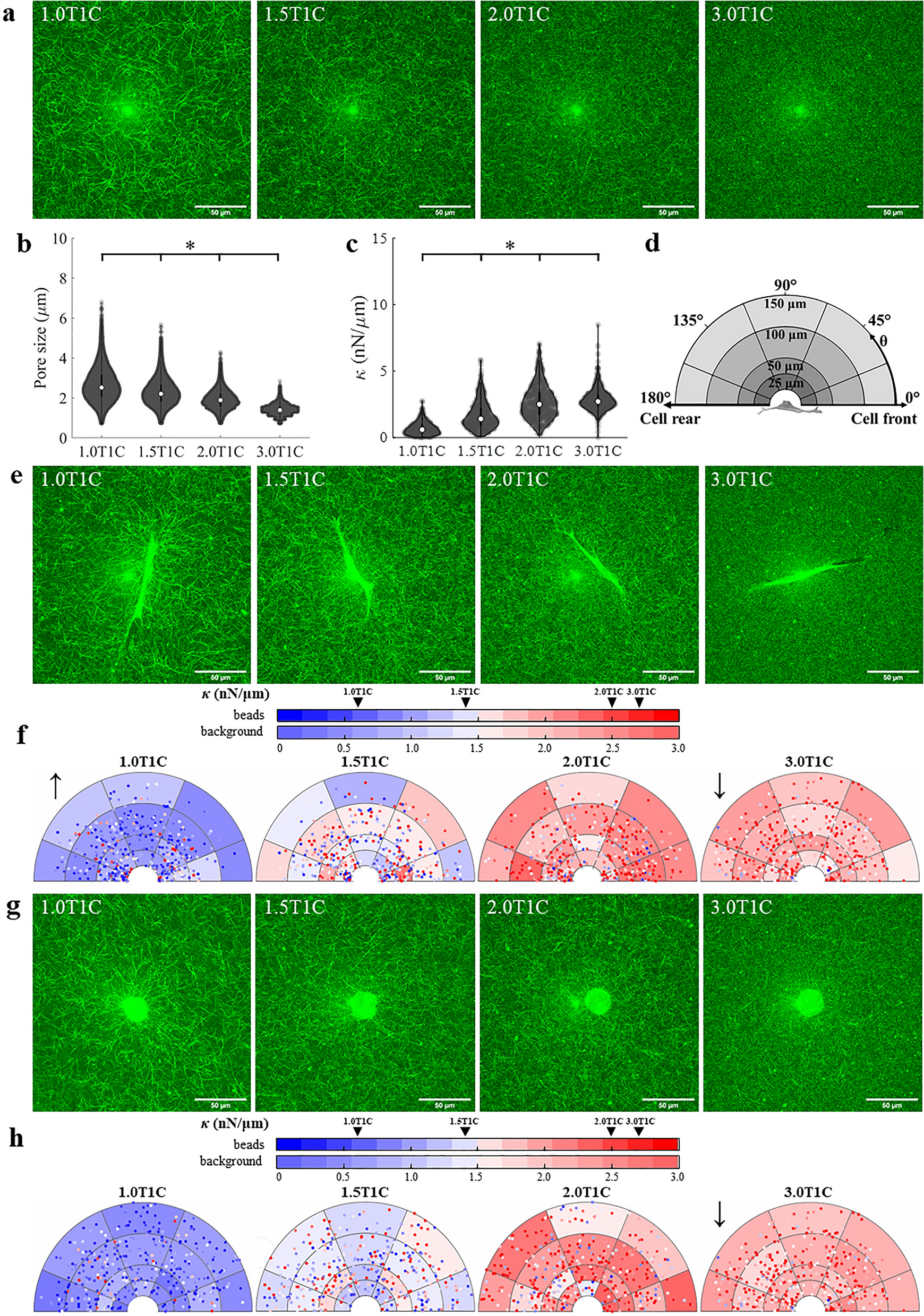
Cell mediated remodeling of stiffness matched collagen and fibrin scaffolds
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

Cell Shape and Durotaxis Explained from Cell-Extracellular Matrix Forces and Focal Adhesion Dynamics - ScienceDirect
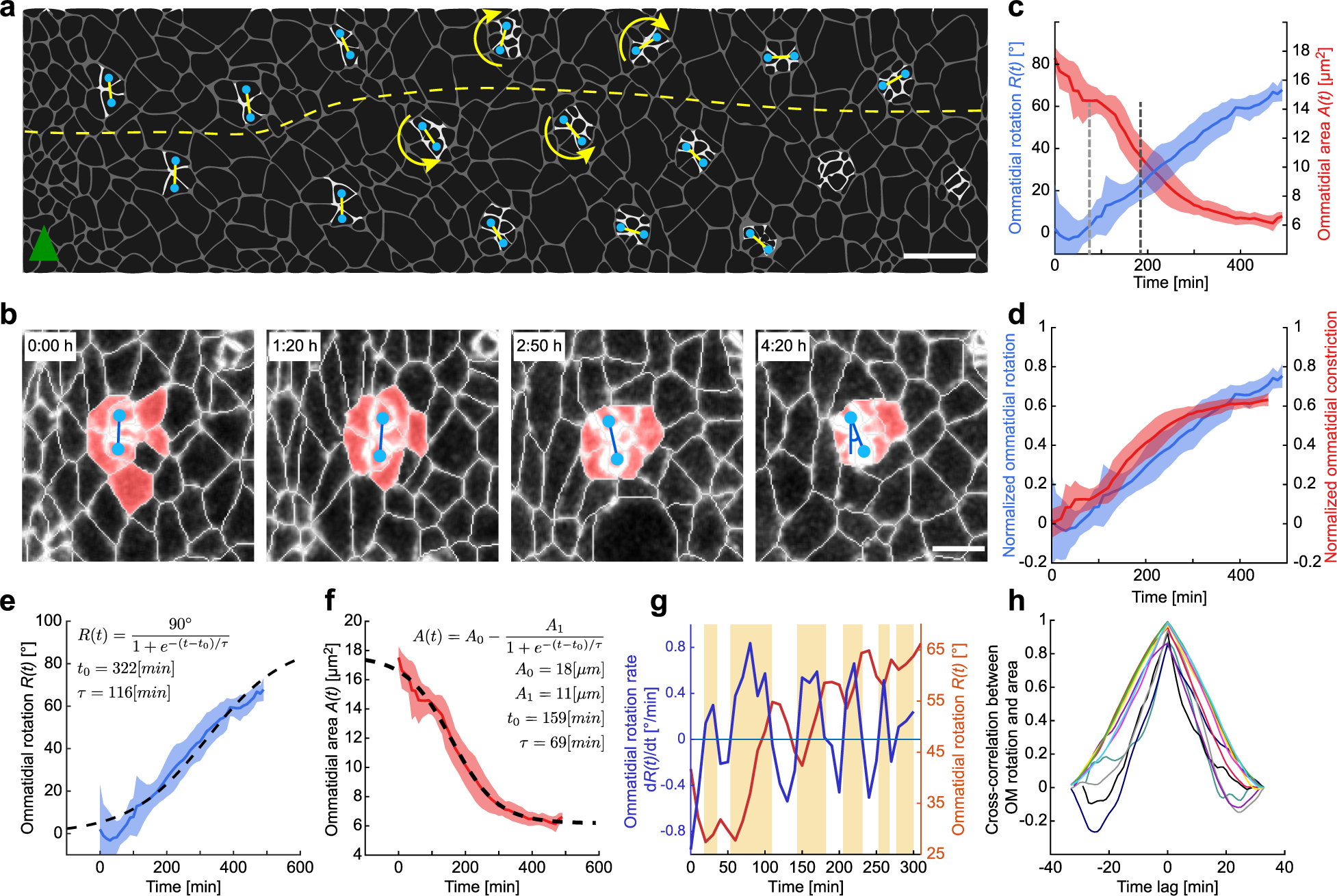
Tissue fluidity mediated by adherens junction dynamics promotes planar cell polarity-driven ommatidial rotation

Cell elongation and tissue length regulation. A. Epithelial cell
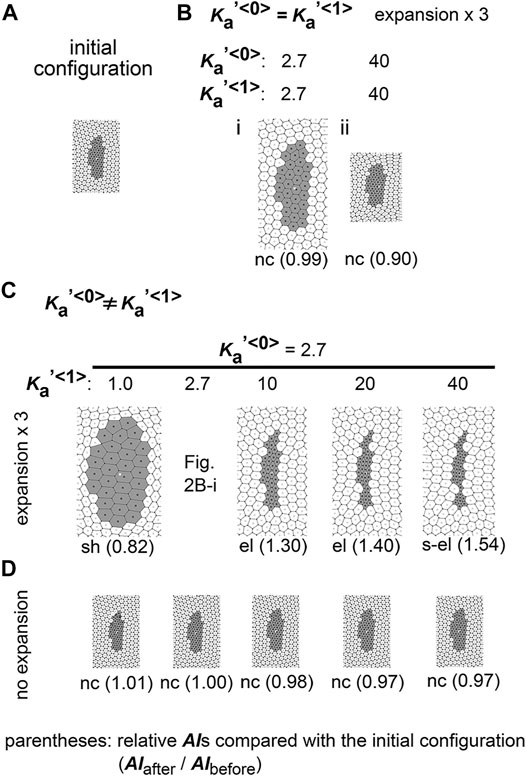
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)