Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
Descrição
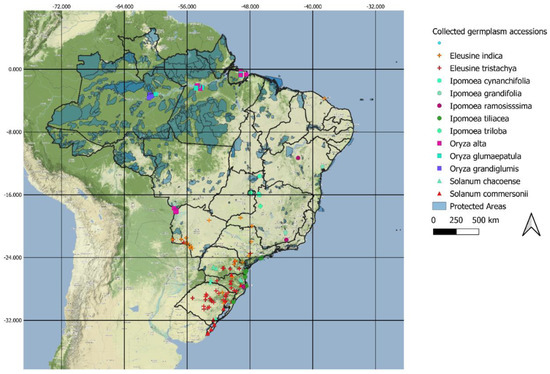
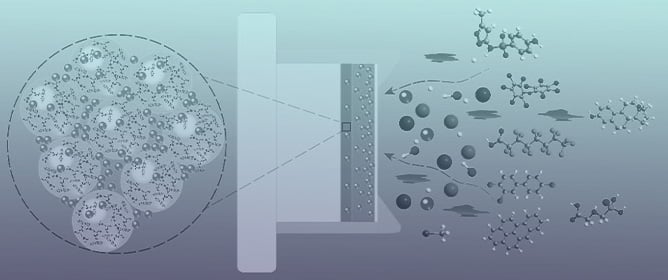
During a fire event, the stability of steel structures may be compromised, and structural collapse may occur due to the loss of their mechanical resistance as the temperature increases. One of the solutions to reduce this problem is the protection with a coating using enhanced fire-resistant mortars. This paper reports a detailed experimental work aiming to develop gypsum and cement-based mortars for passive fire protection and evaluate their composition’s effect in the final thermal performance. Two types of specimens were tested: (i) small specimens composed of a mortar coating (10 mm thick) and one steel plate and (ii) square section short tubular steel columns with 20 mm of coating. The evaluation of the thermal protection was carried out by (a) measuring the thermal gradient between the exposed surface of the protected steel plate under high temperatures and the mortar-steel interface and (b) assessing the fire resistance of the short steel columns. It was concluded that the compositions with gypsum binder present better thermal insulation than the cementitious compositions. Additionally, the introduction of nano- and microparticles of silica still slightly improved the thermal insulation of the tested compositions.
Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science
SFU Applied Sciences

Salem Press - Applied Science

Applied sciences Stock Photos, Royalty Free Applied sciences Images
Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI

Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI

The University of Applied Sciences at Albstadt-Sigmaringen (HSAlbSig) Offers Professional Scrum Master training to Students

Help - PubMed
Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI
Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)