α-Synuclein Aggregation in Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
Descrição
Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide, is characterized by the accumulation of protein deposits in the dopaminergic neurons. These deposits are primarily composed of aggregated forms of α-Synuclein (α-Syn). PD is a complex pathology initially associated with motor deficiencies, as a result of an acute neuronal loss in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), with a significant dopaminergic (DA) impairment.

Cellular models of alpha‐synuclein toxicity and aggregation - Delenclos - 2019 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

Calcipotriol inhibits α‐synuclein aggregation in SH‐SY5Y neuroblastoma cells by a Calbindin‐D28k‐dependent mechanism - Rcom‐H'cheo‐Gauthier - 2017 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library

Targeting Alpha-Synuclein as a Therapy for Parkinson's Disease
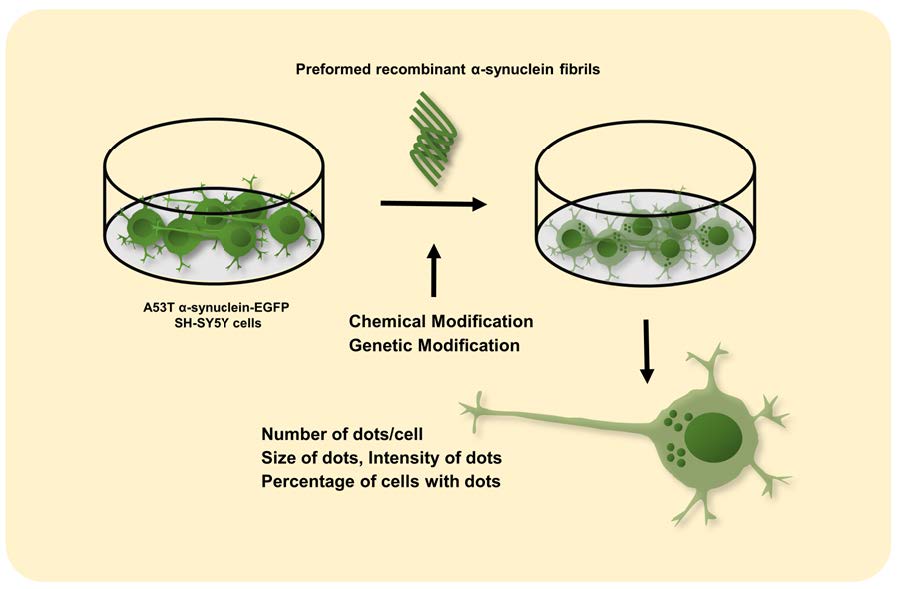
Monitoring α-synuclein Aggregation Induced by Preformed α-synuclein Fibrils in an In Vitro Model System

Exosomal transmission of α-synuclein initiates Parkinson's disease-like pathology

Anti-α-synuclein ASO delivered to monoamine neurons prevents α-synuclein accumulation in a Parkinson's disease-like mouse model and in monkeys - eBioMedicine
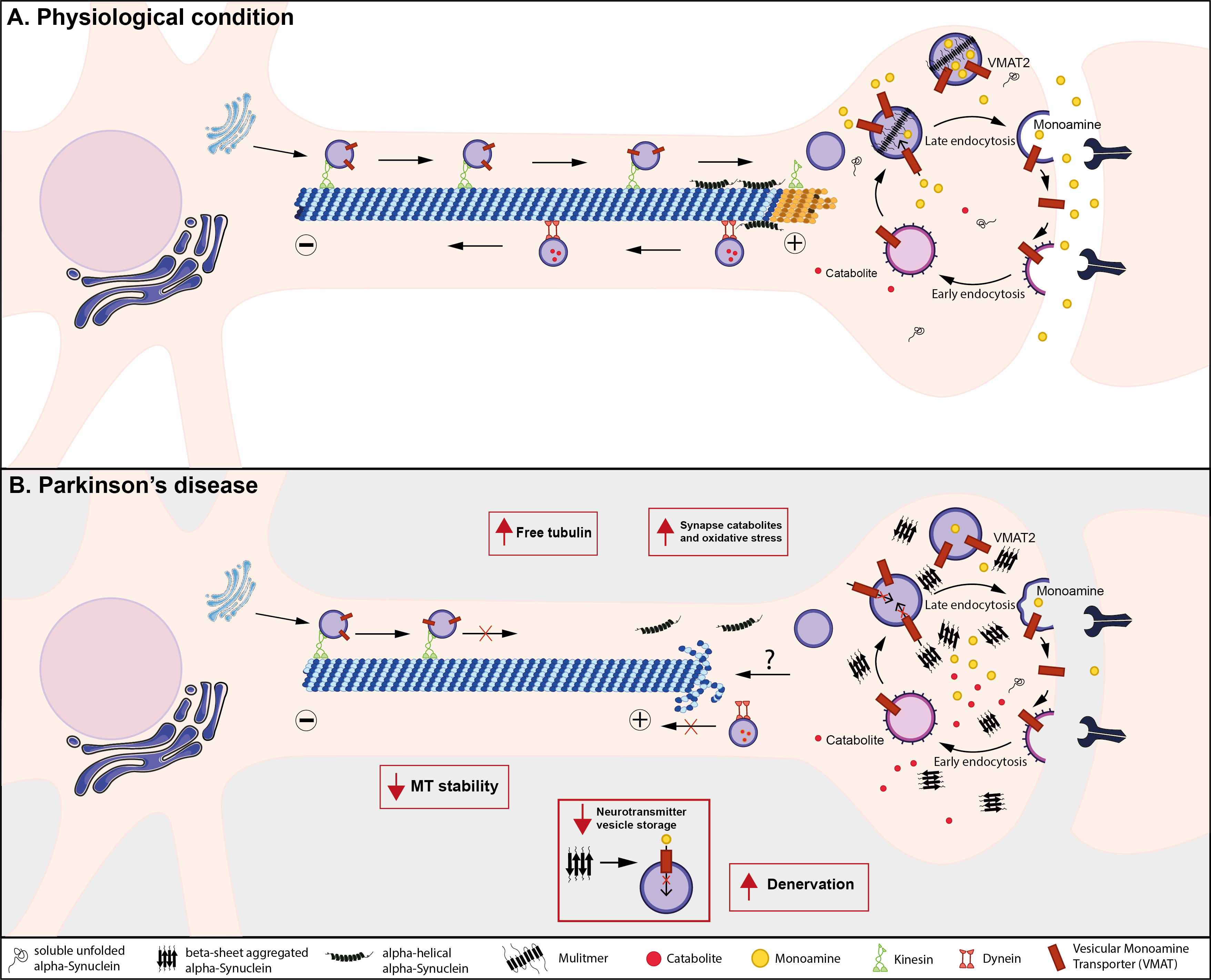
Pathological Pathways and Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease: A View from the Periphery

ISIS Studying the influence of salts on α-synuclein aggregation, a hallmark of Parkinson's disease
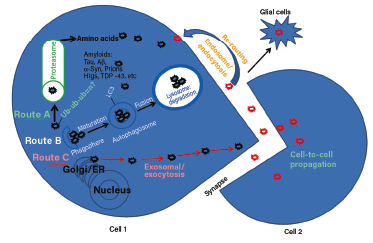
Anti-Alpha-Synuclein Therapies in Parkinson's Disease - Practical Neurology
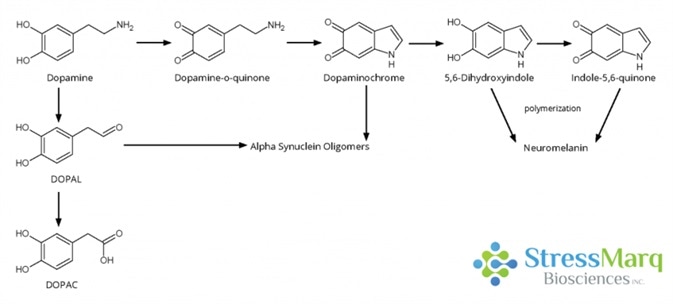
Dopamine Stabilization and Neurodegeneration with Alpha Synuclein Oligomers
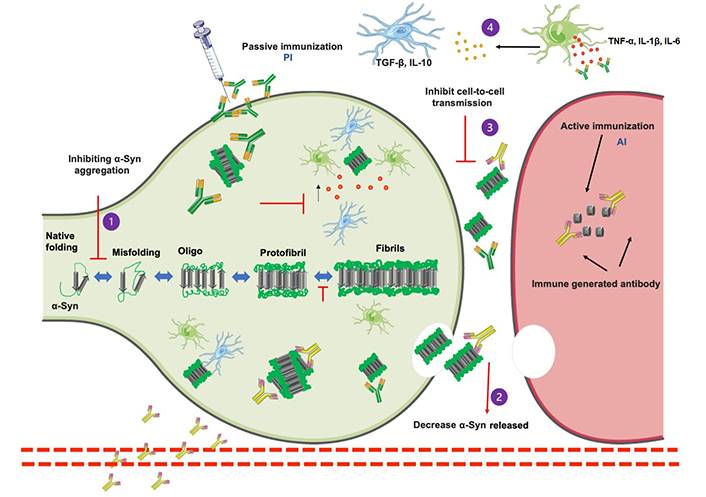
Targeting α-synuclein aggregation with immunotherapy: a promising therapeutic approach for Parkinson's disease
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)